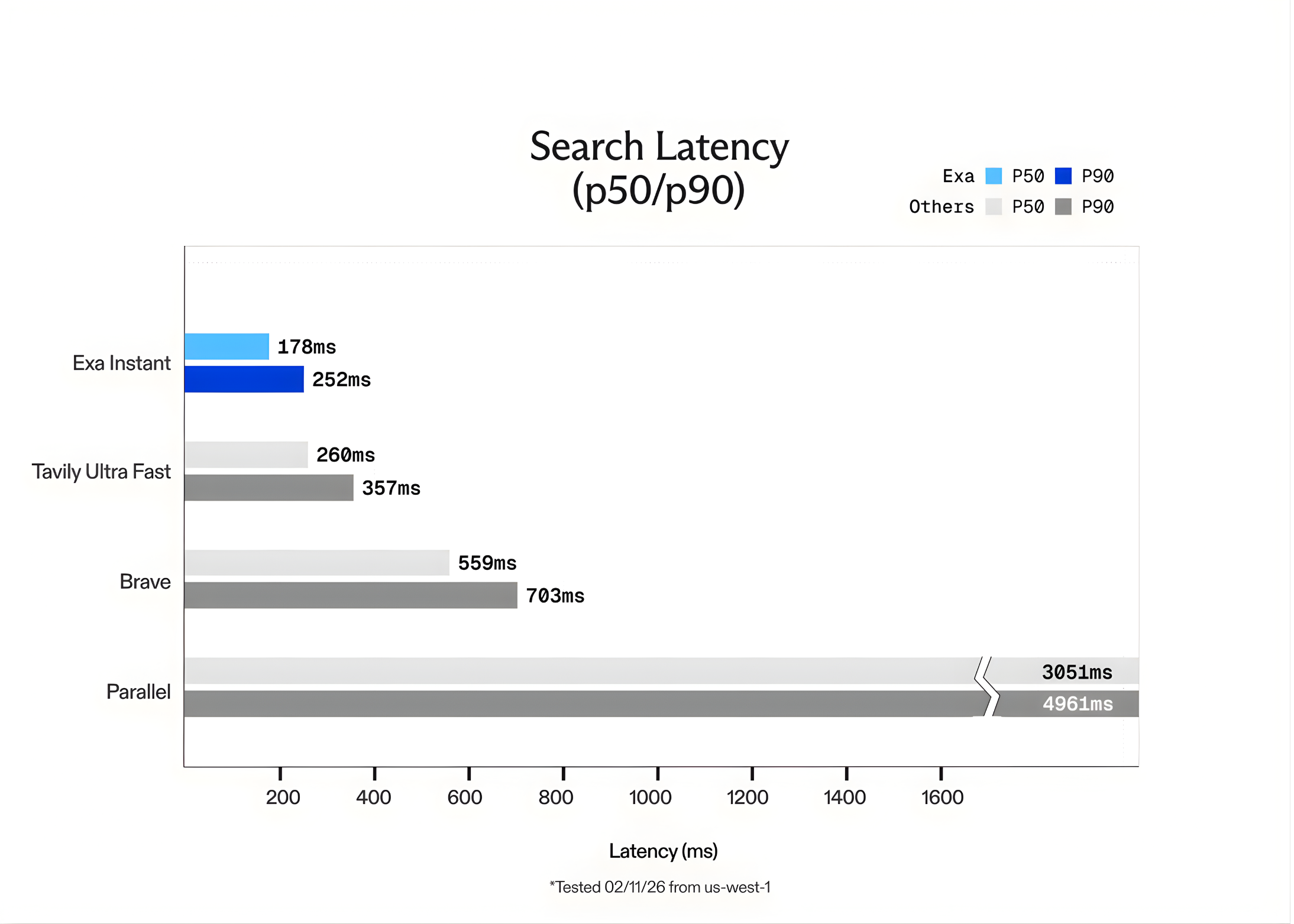
What is Prompt Chaining?

You type long information, more than 500 words, or 1000 words. Build everything well. It explains in detail what needs to be done, down to the fine details of each step. Then press enter. Your AI chatbot starts strong, follows all the instructions from above, then slows down in the middle, and completely forgets some of the instructions at the end. In the end, you have a potpourri of output that is not entirely accurate, but certainly not good enough to use. If you’ve ever used AI in a complex, multi-step process, chances are you’ve gone through something similar. And it often leaves you frustrated, as there isn’t much you can do after filling out the complete information. Well, now, there is. Two words – Quick Exchange.
A way to inform that only a few AI enthusiasts know and use it. Fast chaining is now gaining fame and acceptance for its better results than traditional methods of informing. Here, we’ll explore what it is, how it’s done, and what you can expect while using it.
What is Prompt Chaining?
Fast chain is a different way to inform, and it works amazingly well. It basically requires breaking down one complex task into a series of smaller, focused instructions, to form a “chain” of instructions. This is also where it gets its name – Prompt Chaining.
Note that this series or sequence is constructed in a very specific way. The idea is to include a series of notifications in such a way that the output of each is the input of the next step. So effectively, instead of asking the model to do everything at once, you guide it through a systematic, step-by-step process.
To compare it to a real-life example, think about this: you don’t tell a junior analyst (check how to become a data analyst in 2026 here), “Create a full report, create visuals, analyze trends, and give business recommendations” in one breath. You tear it down. Start by collecting data – Then analyze it – Then extract information – Then prepare a report.
Quick chaining works the same way.
You break your big task down into smaller tasks. Each command handles only one purpose. Once the model has completed that step, you take the output and feed it to the next notification. Finally, the last command combines everything into a polished result. Instead of one big order, you build a structured workflow.
And that changes everything. How? Read on
Why Does It Work? (Problem with Mega Prompts)
Mega information fails for a simple reason: overload.
You saw a glimpse of it in the example above, where a small analyst who issued many instructions at once might not be able to follow them. AI models also face the same challenge.
When you give a model 20 instructions at once – edit this, add examples, keep it short, use this tone, enter data, avoid fluff – it tries to satisfy everything at once. The beginning looks strong because the instructions are new. But as the response grows longer, the model begins to prioritize some constraints over others.
This is where the model begins to drift. It is then that he begins to forget things.
Large notifications naturally cause this problem. They include many goals and obstacles. They ask the model to think, write, edit, prepare, and polish, all in one pass. So, naturally, after a point, it shows or is completely forgotten.
Another issue is ambiguity. Over time, some instructions quietly conflict with others. The model makes a choice, and it may not be what you intended.
A fast blockchain is a great solution to both of these problems. It simply reduces the cognitive load. One job. One focus. One output at a time.
Which means – less confusion, more clarity, and better results.
Why is it better?
Advantages of Prompt Chaining
– The biggest benefit of fast binding is Focus.
With one big instruction, AI models tend to mix everything up, slip, and make mistakes. The result is an inevitable loss of quality.
Quick chaining eliminates that overload.
Each step has one clear purpose. The model focuses only on that function. The result? Clean effects, optical illusions, and very little editing.
– Yet another benefit is Control.
With chaining, you review the output of each stage. If something is tangible, fix it early instead of finding the problem at the end of a 1,000 word answer. This makes the process repetitive rather than efficient.
And perhaps most importantly, combining mirrors how the actual workflow works. Do your research first. Then build, expand, refine, and finish. Therefore, it is possible that you are not only encouraging but explaining the process.
And routines outpace smart instructions all the time.
A Real Example of Fast Bonding
Let me demonstrate these benefits of fast binding in a real use case. Let’s say you want to write a high-quality blog post on “AI in Healthcare.” We will use one mega prompt followed by a prompt chain. I will also share the output of each step as we go.
So, with mega information, most people, including me until recently, would write something like this:
“Write a 1200 word SEO optimized blog, analyzing AI in healthcare with examples, data, future trends, and a strong conclusion.”
Here is the output of such mega data:
Next, let’s try to combine it to get a better result. One obvious way to do this is as follows.
Prompt 1: “List 10 important problems that AI is solving in healthcare today.”
Note 2: “From this list, group them into 4 logical parts of the blog outline.”
Prompt 3: “Extend Paragraph 1 to 300 words with one real-world example and supporting data.”
Prompt 4: “Now extend section 2 in the same way.”
Prompt 5: “Extend paragraphs 3 and 4”
Instruction 6: “Match all this with an appropriate introduction and conclusion, both 100 words each.”
Notice the difference.
The end result in the quick assembly is very good and fits what we really needed. It’s a much better read, has the topics covered the way we wanted, and is clear and concise. This was possible because instead of trusting the model to handle everything at once, we guided it step by step. Each output improved the next.
Same model. Different workflows. A completely different result.
X user GodofPrompts, in a series, shares many such benefits of meeting quickly over mega prompts. Here’s what user reviews say so far.
| Metric | Mega Prompt method | Prompt Chaining Method |
|---|---|---|
| Results That Require Major Planning | 8 out of 10 | 2 out of 10 |
| Average Inhalation Rate | ~40% | ~8% |
| Draft Deadline | 45 minutes | 22 minutes |
The user even claims that the output quality has increased by 67% since he started using fast chaining.
So, now that you know that quick chaining has a huge advantage over mega information, here’s how (and where) you can use it for maximum effect.
Where to Use Prompt Chaining
Quick chaining shines in many multi-stage operations. If a project requires thinking, planning, expanding, refining, and finalizing, chaining will almost always be better than a single mega-data.
Here are some high-impact areas where it works best:
1. Creating content
How to do it – First, generate ideas → then build structure → expand categories → improve tone → Finally, prepare SEO or platform style.
2. Restart Build
How to do it – First, remove keywords from the job description → then rewrite the transaction → shape categories → configure ATS → polish for final formatting.
3. Research & Analysis
How to do it – Collect data points → cluster themes → analyze data → challenge assumptions → summarize findings.
4. Coding and debugging
How to do it – Split the feature into modules → write individual functions → test limit values → refactor → document.
5. Business & Strategy Reports
How to do it – List problems → prioritize impact → suggest solutions → stress test risks → create executive summary.
In short, use fast chaining whenever your output needs depth, structure, or precision.
Here is a quote to remember:
If it’s complicated, chain it.
The conclusion
Fast bonding is not a trick or a secret command. And it’s definitely not about writing the “smartest” commands. Basically, it’s about designing smart workflows. Mega information fails because it overloads the system. Fast chaining removes that stress and breaks complexity into clarity. One goal at a time. A better result, therefore, is not just a better output but a better process.
As AI tools become more powerful, the advantage will no longer belong to the person who writes the longest information. It will be for someone who creates a very clean workflow. So the next time you feel tempted to write a 1,000-word block of instructions, pause. And build the result step by step. Because in the age of AI, process beats inspiration.
Sign in to continue reading and enjoy content curated by experts.