Building a Self-Developing AI Agent with Langfuse

Building an LLM prototype immediately. A few lines of Python, fast, and it works. But Productivity is a whole different game. You start to see vague responses, hallucinations, latency spikes, and the odd failure where the model clearly “knows” something but continues to make mistakes. Since everything works probabilistically, debugging becomes difficult. Why did the search for boots turn into shoes? The system makes a choice, but you can’t easily track the thinking.
To deal with this, we will build FuseCommercean advanced e-commerce support system designed for visibility and control. Using Langfuse, we will create a logical workflow with semantic search and purposeful planning, while keeping all decisions transparent. In this article, we will turn a weak prototype into a physical, production-ready LLM system.
What is Langfuse?
Langfuse serves as an open source platform for LLM engineering that allows teams to work together on debugging and analyzing and improving their LLM applications. The platform works like DevTools for AI agents.
The program provides three main functions including:
- Tracks that show all the way through the program including LLM calls and database queries and tool usage.
- Metrics deliver real-time monitoring of latency and cost and token usage.
- A survey that collects user feedback through a thumbs-down system that connects directly to the specific generation that generated the feedback.
- The system enables testing with Dataset Management that allows users to organize their test inputs and outputs.
In this project Langfuse serves as our main logging system which helps us to create an automated system that improves its performance.
What we create: FuseCommerce…
We will be developing an intelligent customer support representative for the retail business with a technology called “FuseCommerce.”
In contrast to the standard LLM wrapper, the following features will be included:
- Path of the Mind – Ability to analyze (think) what you are saying before responding – including finding the reason(s) for the interaction (ie, wanting to buy something vs checking out an order vs wanting to talk about something).
- Semantic memory – Ability to recognize and represent ideas as concepts (eg: how “play gear” and “Machine Mouse” are conceptually connected) through vector embedding.
- Visual Reasoning (includes a stunning user interface) – How to show (to the customer) what the agent is doing.
Langfuse’s role in the project
Langfuse is the core of the agent used for this task. It allows us to follow the unique steps of our agent (objective classification, retrieval, production) and shows us how they all work together, allowing us to identify where something went wrong if the response is incorrect.
- Traceability – We will want to capture all agent steps in Langfuse using spaces. If the user receives an incorrect response, we can use time tracking or tracing to identify where the error occurred in the agent process.
- Session Tracking – We will capture all interactions between the user and the agent within a single group identified by “
session_id“In the Langfuse dashboard to allow us to replay all user interactions in context. - A feedback loop – We will build user feedback buttons directly into the track, so if a user downvotes an answer, we will be able to quickly find out what feedback or notification the user experienced that led to them downvoting the answer.
Getting started
You can quickly and easily start the agent installation process.
What is required
Installation
The first thing you need to do is install the following dependencies including Langfuse SDK and Google Generative AI.
pip install langfuse streamlit google-generativeai python-dotenv numpy scikit-learn 
Configuration
After you finish installing the libraries, you will need to create a .env file where your information will be stored in a secure manner.
GOOGLE_API_KEY=your_gemini_key
LANGFUSE_PUBLIC_KEY=pk-lf-...
LANGFUSE_SECRET_KEY=sk-lf-...
LANGFUSE_HOST=
How to Build?
Step 1: Semantic knowledge base
A traditional keyword search can break down if the user uses different words, i.e., the use of synonyms. So, we want to use Vector Embeddings to build a semantic search engine.
In absolute terms, that is, Cosine Similarity, we will create a “vector of meaning” for each of our products.
# db.py
from sklearn.metrics.pairwise import cosine_similarity
import google.generativeai as genai
def semantic_search(query):
# Create a vector representation of the query
query_embedding = genai.embed_content(
model="models/text-embedding-004",
content=query
)["embedding"]
# Using math, find the nearest meanings to the query
similarities = cosine_similarity([query_embedding], product_vectors)
return get_top_matches(similarities)
Step 2: The “brain” of the smart router
When users say “Hello,” we are able to distinguish the user’s intent using a classifier to avoid searching the database.
You’ll see that we also automatically detect input, output, and latency using the @langfuse.observe the decorator. Like magic!
@langfuse.observe(as_type="generation")
def classify_user_intent(user_input):
prompt = f"""
Use the following user input to classify the user's intent into one of the three categories:
1. PRODUCT_SEARCH
2. ORDER_STATUS
3. GENERAL_CHAT
Input: {user_input}
"""
# Call Gemini model here...
intent = "PRODUCT_SEARCH" # Placeholder return value
return intent
Step 3: Agent workflow
We put our process together. The agent will perceive, receive input, think (Distribute) and Take (Route).
We use the method lf_client.update_current_trace tagging the conversation with metadata information such as session_id.
@langfuse.observe() # Root Trace
def handle_customer_user_input(user_input, session_id):
# Tag the session
langfuse.update_current_trace(session_id=session_id)
# Think
intent = get_classified_intent(user_input)
# Act based on classified intent
if intent == "PRODUCT_SEARCH":
context = use_semantic_search(user_input)
elif intent == "ORDER_STATUS":
context = check_order_status(user_input)
else:
context = None # Optional fallback for GENERAL_CHAT or unknown intents
# Return the response
response = generate_ai_response(context, intent)
return responseStep 4: User interface and feedback system
We are building an improved user interface for Streamlit. A key change is that the feedback buttons will provide a feedback result back to Langfuse based on the tracking ID associated with a particular user conversation.
# app.py
col1, col2 = st.columns(2)
if col1.button("👍"):
lf_client.score(trace_id=trace_id, name="user-satisfaction", value=1)
if col2.button("👎"):
lf_client.score(trace_id=trace_id, name="user-satisfaction", value=0)Input, Output and Results Analysis
Let’s take a closer look at the user’s question: “Do you sell any accessories for game systems?”
- An investigation
- User: “Do you sell any accessories for game systems?”
- Context: There is no exact match for the keyword “accessory”.
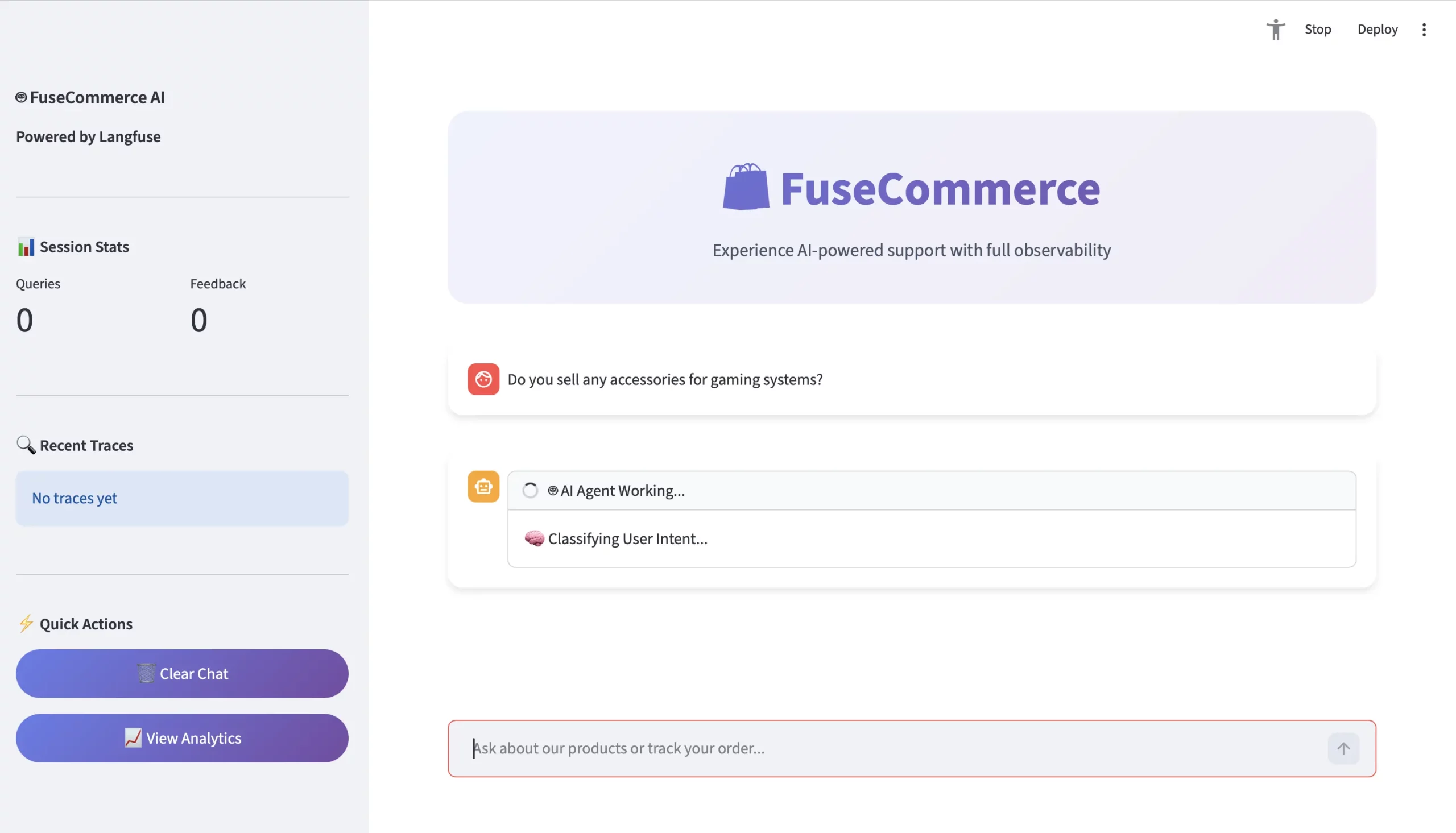
- Trace (Langfuse Point of Perspective)
Langfuse will create the following view to visualize the nested hierarchy:
TRACE: agent chat (1.5 seconds)
- Generation: classify_intent –> Output = PRODUCT_SEARCH
- The span: retrieve_knowledge –> Semantic Search = geometrically maps game data to Quantum Wireless Mouse and UltraView Monitor.
- Generation: generate_ai_response -> Output = “Yes! For gaming applications, we would recommend the Quantum Wireless Mouse…”
- Analysis
If the user clicks the thumbs up, Langfuse gets 1 point. You will have the total number of thumbs clicks per day to view the daily average. You will have a cumulative view dashboard to view:
- Average latency: Is your semantic search slow??
- Objective Accuracy: Is the route a dream??
- Cost / Session: How much does it cost to use Gemini??
The conclusion
Through our implementation of Langfuse we have transformed a hidden chatbot system into an active virtual system. We have built user trust through our product development.
We have shown that our agent has the ability to “think” using Intent Programming while it can “understand” things through Semantic search and can “find” information through the results of user feedback. This architecture serves as the foundation for modern AI systems operating in real-world environments.
Frequently Asked Questions
IA. Langfuse provides tracking tools, metrics, and evaluation tools to debug, monitor, and improve LLM agents in production.
A. It uses objective classification to find the type of query, and then routes to semantic search, hierarchical ordering, or general discussion.
A. User feedback is logged on a per-track basis, allowing for performance monitoring and iterative optimization of information, retrieval, and routing.
Sign in to continue reading and enjoy content curated by experts.



